
- JPROFILER MEMORY LEAK TUTORIAL HOW TO
- JPROFILER MEMORY LEAK TUTORIAL SERIAL
- JPROFILER MEMORY LEAK TUTORIAL FULL
- JPROFILER MEMORY LEAK TUTORIAL CODE
- JPROFILER MEMORY LEAK TUTORIAL FREE
With EJ Technologies JProfiler 2020 serial key, users can optimize and improve their software performance and develop great software. It has the ability to handle large software projects and small projects. Using consumption reports, users can eliminate bottlenecks, large memory, multi-threading issues, and parallel processing. Users can also monitor different Java applications that are running for progress reports.
JPROFILER MEMORY LEAK TUTORIAL FULL
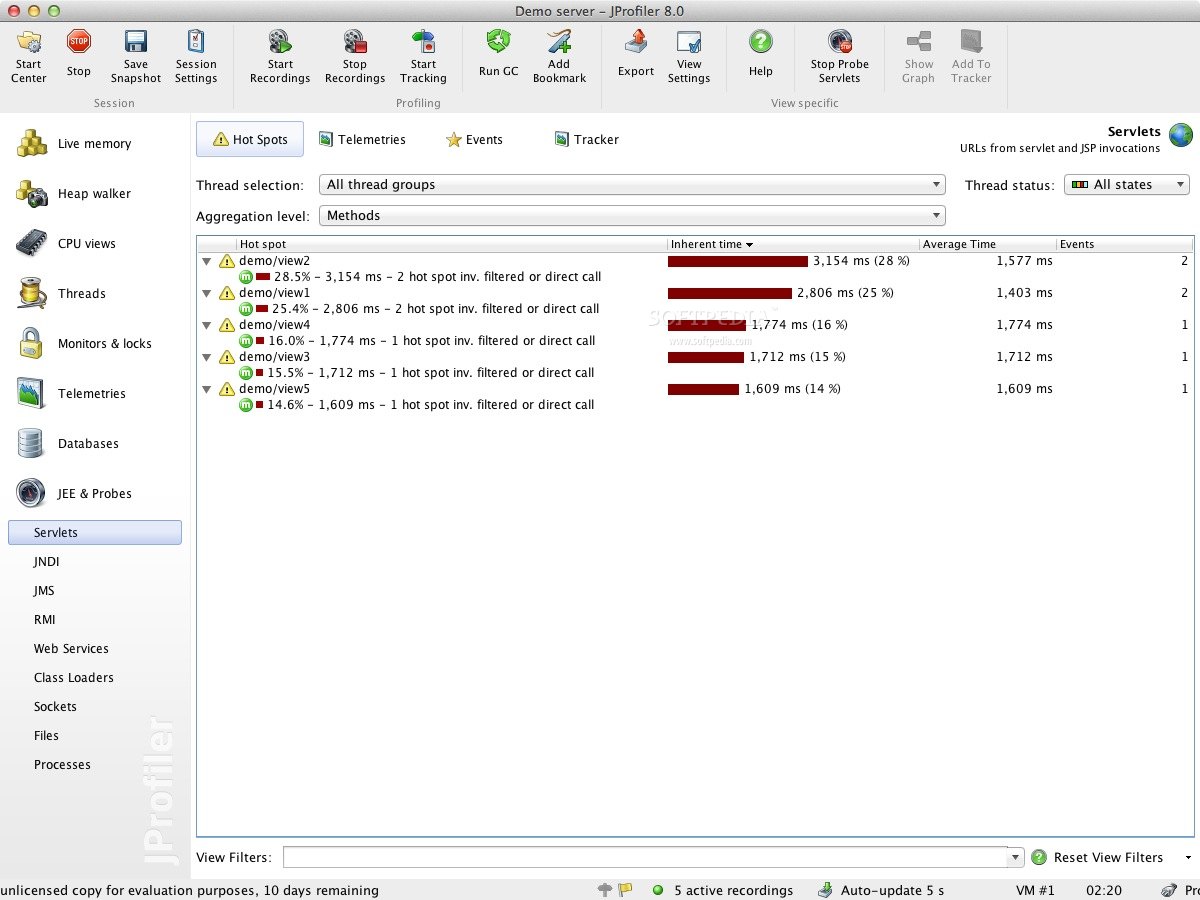
And what’s more, all these views are also available for your own custom probes that you can configure on the fly within JProfilerĮJ Technologies JProfiler Full Version has a modern and elegant user interface that enables users to operate this application easily and reliably. Each of these probes has its own set of useful views that gives you general insight, highlights performance problems and allows you to trace single events. In addition to the Java EE subsystems like JDBC, JPA/Hibernate, JSP/Servlets, JMS, web services and JNDI, JProfiler also presents high-level information about RMI calls, files, sockets, and processes.
JPROFILER MEMORY LEAK TUTORIAL FREE
Everything else is unused and can be thrown away.Download NOW EJ Technologies JProfiler 11.1.5 Crack Free DownloadĮJ Technologies JProfiler Crack has a number of probes that show you higher level data from interesting subsystems in the JRE.
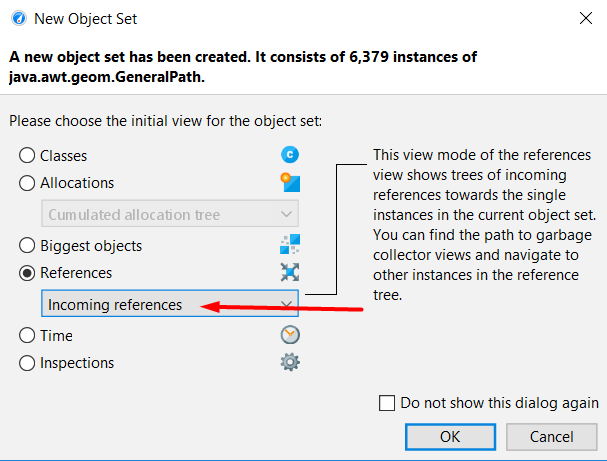
The above process is repeated until all objected that can be transitively reached from GC roots are visited and marked as “in use”.

One object can reference another in different ways in Java, most commonly being when object A is stored in a field of object B.
JPROFILER MEMORY LEAK TUTORIAL CODE
They are, for example, currently executing method’s local variables and input parameters, application threads, references from native code and similar “global” objects. These are called GC roots and are (almost) never discarded.
JPROFILER MEMORY LEAK TUTORIAL HOW TO
Looking for an easy solution to a Java memory leak? Plumbr automatically detects the leak and tells you how to solve it. In this post I will explain why memory leaks are in fact a common problem for Java applications. But when we add Java into the equation, the initial excitement is often complemented with questions: “Are there memory leaks in Java? Isn’t Java a garbage-collected language?” When we talk to people about our solution for discovering memory leaks we immediately get positive feedback.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
